Publications from 1995 to 2003
- TCHLab
- Jan 1, 1995
- 5 min read
Updated: Aug 11, 2019
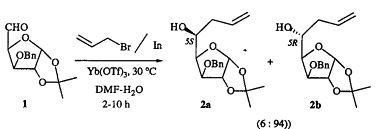
R. B. Wang, C. M. Lim, C. H. Tan, B. K. Lim, K. Y. Sim and T. P. Loh. Ytterbium trifluoromethanesulfonate [Yb(OTf)3] promoted indium mediated allylation reactions of carbonyl-compounds in aqueous-media. Tetrahedron-Asymmetry, 1995, 6, 1825 – 1828.
Abstract: Indium-mediated allylation reactions of the sugar derivative 1 in aqueous media have been found to proceed with high anti diastereofacial selectivity in the presence of ytterbium trifluoromethanesulfonate as Lewis acid.
Download paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/0957-4166(95)00228-H
N. Srikanth, C. H. Tan, S. C. Ng, T. P. Loh, L. L. Koh and K. Y. Sim. Synthesis of heterocyclic analogues of tamoxifen as potential anti-estrogens. Journal of Chemical Research-S, 1997, 8, 274 – 275; Journal of Chemical Research-M, 1997, 1828 – 1849.
Abstract: The synthesis of (E/Z)-1-aryl-2-phenyl-1-(2-thienyl/selenophen-2-yl)but-1-enes, derived from 2-phenyl-1-(2-thienyl/ selenophen-2-yl)butan-1-ones, is described; the key steps in the synthesis involve the reaction of the butan-1-ones with 4-(2-morpholinoethoxy)phenyl bromide, followed by dehydration of the resulting carbinols to give the target compounds which are separated by fractional recrystallisation.
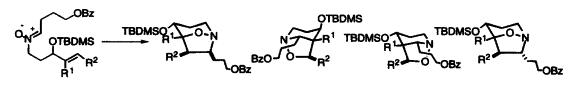
W. P. Hems, C. H. Tan, T. Stork, N. Feeder and A. B. Holmes. Intramolecular cyclisation of (Z)-N-4-alkenylnitrones and the effects of alkenyl substituents. Tetrahedron Letters, 1999, 40, 1393 – 1396.
Abstract: The intramolecular 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions of (Z)-N-4-alkenylnitrones carrying various alkenyl substituents were investigated, and the regiochemistry of the resulting isoxazolidines was determined. Silyl- and bromo-substituents were found to effect significant regiocontrol on the intramolecular nitrone dipolar cycloaddition reaction. The intramolecular dipolar cycloaddition of (Z)-N-4-alkenylnitrones with substituted olefins was investigated and the regiochemistry of the resulting isoxazolidines was determined.
Download paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(98)02617-3
C. H. Tan, T. Stork, N. Feeder and A. B. Holmes. Stereoselective synthesis of the indolizidine core of the allopumiliotoxins. Tetrahedron Letters, 1999, 40, 1397 – 1400.
Abstract: The common indolizidine core leading to the allopumiliotoxins was synthesized using an intramolecular (Z)-N-4-alkenylnitrone cycloaddition reaction as the key step. The synthesis began with (R)-tert-butyl-3-hydroxy-pent-4-enoate which was obtained via enzymatic resolution using Amano PS lipase. The common intermediate to the allopumiliotoxins, the indolizidine core, was synthesized using an intramolecular (Z)-N-4-alkenylnitrone cycloaddition reaction as the key step.
Download paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(98)02618-5
Y. Kobayashi, C. H. Tan and Y. Kishi. Toward creation of a universal NMR database for stereochemical assignment: the case of 1,3,5-trisubstituted acyclic systems. Helvetica Chimica Acta, 2000, 83, 2562 – 2571.
Abstract: Using the diastereoisomeric triols 1a – d (Fig. 1) and examples summarized in Fig. 2, the central C‐atom of acyclic 1,3,5‐triols is demonstrated to exhibit a distinctive chemical shift that is dependent on the 1,3‐ and 3,5‐relative configuration, but is independent of the functionalities present outside of this structural motif. These NMR characteristics are then used to predict the relative configuration of several natural products (Fig. 7). In addition, an example is given to show the possibility of assembling an NMR database for a larger array of functional groups from NMR databases of smaller arrays of functional groups.
Y. Kobayashi, C. H. Tan and Y. Kishi. Stereochemical assignment of the C21-C38 portion of the Desertomycin/Oasomycin class of natural products via universal NMR databases: Prediction. Angewandte Chemie International Edition English, 2000, 39, 4279 – 4281.
Abstract: Stereochemistry can be predicted: The stereoselective synthesis of the C21-C38 degradation product derived from oasomycins A and B has confirmed the stereochemistry predicted from a comparitive study of the NMR chemical shifts of the C21-C38 portion of the natural products with those obtained for its diastereomers.
C. H. Tan, Y. Kobayashi and Y. Kishi. Stereochemical assignment of the C21-C38 portion of the Desertomycin/Oasomycin class of natural products via universal NMR databases: Proof. Angewandte Chemie International Edition English, 2000, 39, 4282–4284
Abstract: The stereoselective synthesis of the C21–C38 degradation product derived from oasomycins A and B (see picture) has confirmed the stereochemistry predicted from a comparitive study of the NMR chemical shifts of the C21–C38 portion of the natural products with those obtained for its diastereomers.
C. H. Tan and A. B. Holmes. Total synthesis of allopumiliotoxin 323B'. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2001, 7, 1845 – 1854.
Abstract: This paper describes the synthesis of (+)‐allopumiliotoxin 323B′ (1) using the intramolecular [3+2]‐cycloaddition reaction of the (Z)‐N‐alkenylnitrone 4. This synthesis began with (R)‐tert‐butyl‐3‐hydroxy‐pent‐4‐enoate [(R)‐13] which was obtained by enzymatic resolution with Amano PS lipase. A series of manipulations gave intermediate 17 and in situ coupling with 4‐benzoyloxybutanal lead to the (Z)‐N‐alkenylnitrone 4 which underwent an intramolecular [3+2]‐cycloaddition reaction to give the isoxazolidine 3 as the major cycloadduct. Isoxazolidine 3 provided the piperidinone 24 which upon diastereofacial selective addition of MeMgBr gave the required tertiary alcohol 25. Formation of the indolizidine core 2 was achieved by an intramolecular SN2 reaction. The side chain was assembled from a Wittig reaction between the phosphorane 8 and the enantiomerically pure aldehyde 9. Further modifications afforded the aldehyde 7 which underwent an aldol condensation with the potassium enolate of the indolizidone core 2. Dehydration gave the enone 37 which was converted into the anti‐diol 38 by intramolecular hydride reduction. Finally, deprotection of the BOM protecting group gave (+)‐allopumiliotoxin 323B′ (1).
Paper download: http://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3765(20010504)7:9<1845::AID-CHEM1845>3.0.CO;2-2
Y. Kobayashi, C. H. Tan and Y. Kishi. Toward creation of a universal NMR databases for stereochemical assignment: Complete structure of the Desertomycin/Oasomycin class of natural products, Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2001, 123, 2076 – 2078.
Abstract: Through the work on palytoxin,1 AAL toxins/fumonisins,2 and maitotoxin,3 we have experimentally demonstrated that the structural properties of fatty acids and related compounds are inherent to the specific stereochemical arrangements of (small) substituents on their carbon backbone and are independent from the rest of the molecule. It has been shown that steric and stereoelectronic interactions between structural clusters connected either directly or with a one-methylene bridge are significant, whereas interactions between structural clusters connected with a two- or more-methylene bridge are almost negligible. On the basis of these experimental results, the concept of a universal NMR database approach for stereochemical assignment has been advanced.
Paper download: https://doi-org/10.1021/ja004154q
Y. Kobayashi, N. Hayashi, C. H. Tan and Y. Kishi. Toward the creation of NMR databases in chiral solvents for assignments of relative and absolute stereochemistry: Proof of concept. Organic Letters, 2001, 3, 2245 – 2248.
Abstract: An NMR database approach in a chiral solvent allows us to predict both relative and absolute stereochemistry of an unknown compound without degradation and/or derivatization. N,α-Dimethylbenzylamine (DMBA) is a suitable solvent for this purpose. Using the C.5−C.10 portion of oasomycin A, the feasibility and reliability of this approach is demonstrated.
Paper download: https://doi-org/10.1021/ol010108z
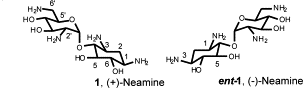
D. H. Ryu, C. H. Tan and R. R. Rando. Synthesis of (+), (-)-Neamine and their positional isomers as potential antibiotics. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2003, 13, 901 – 903.
Abstract: The syntheses of (+)-neamine 1, (−)-neamine ent-1 and their positional isomers 2, 3, ent-2 and ent-3 are reported as potential new scaffolds for novel aminoglycoside antibiotics. These isomers exhibit similar inhibitory activities, as shown using an in vitro translation assay. A simple model is proposed to explain this lack of stereospecific binding to the ribosomal RNA.
Paper download: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-894X(02)01073-9







Comments